Site Navigation
Oilfield expertise at your desktop
Traps
Traps are the configuration of rocks which are suitable for preventing further migration of hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons are unable to migrate, as they are sealed by a relatively impermeable formation. Traps are broadly classified as 1.Structural traps, 2.Stratigraphic traps and 3.Combination traps.
Structural traps occur in deformed strata such as folds or faults and stratigraphic traps occur in zones such as unconformities, pinch-outs and reefs. Sometimes sealing of hydrocarbon occurs by combination of both stratigraphic and structural traps. These types of traps are called combination traps.
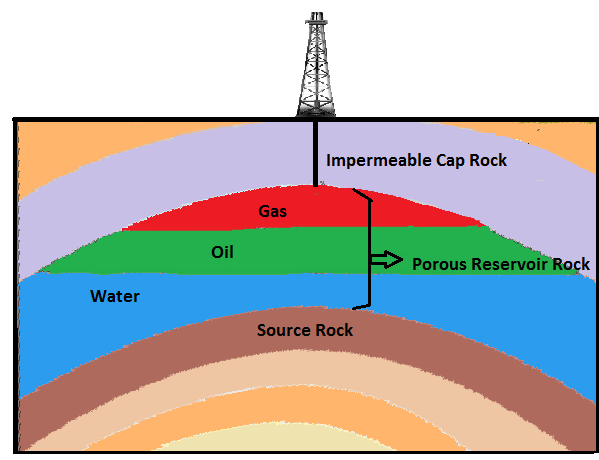
A trap is an integral constituent of a petroleum system. Buoyancy makes the petroleum transfers upwards and laterally from source to reservoir. Petroleum will effectively displace groundwater and flow upwards, as it is lighter than water. It will also flow laterally and will seep to the surface through faults and porous overburden unless confined under special circumstances to become trapped and form economic petroleum deposits.
Cap rock is an impermeable formation which aids in prevention of further upward migration of hydrocarbon by buoyancy. It also seals petroleum within reservoir. These rocks are commonly shale’s or chemically precipitated evaporate deposits like salt or gypsum. Due to the possibility of creation of hydrocarbon reservoir below caprock, they are the primary targets for petroleum geologist
Structural Traps
The structural traps are formed due to structural changes happening below surface of earth mainly due to tectonic forces.The structural trap is formed by positioning of porous reservoir and impermeable cap rock due to tectonic forces in such a way that they stop further migration of hydrocarbon and create economic hydrocarbon deposit within fold or a fault.
Structural traps represent the majority of reservoir discovered around the world. Three basic types of structural traps are 1.Anticlinal traps, 2.Fault traps and 3.Salt dome traps.

Figure:- Anticlinal Trap
Stratigraphic traps
Stratigraphic traps are formed due to variations in porosity, lithology, thickness and texture of rock in different formations. These variations are lateral as well as vertical. Porous reservoir may get superimposed by impermeable cap rock due to depositional changes in grain size of different sediments. Stratigraphic traps may happen due to thinning of lenses of sand, morphology of carbonate reefs in sub-circular mounds resulting into reef trap or by juxtaposition of rock types at unconformity surfaces (unconformity traps).

Figure:- Stratigraphic trap
Combination traps
Stratigraphic traps in the rising salt–dome which is draped against the edge with normal-fault trap. The reason behind is the tension stress over the top. In the porous cap of salt dome, some oil also accumulates.

Figure:- Combination trap